The population of obese people in world increased from 10.5 crores in 1975 to 64.1 crores in 2014. In 1975 India ranked 19th in obesity in the world. Now we rank 5th in males and 3rd in females! There were 41.5 crore diabetics in the world in 2015. In India, prevalence of diabetes in the age group of people above 20 years is 8.7%.
Let's know first what obesity and diabetes is...
Role of insulin in diabetes and obesity
Insulin is a chemical substance scientifically termed as hormone from a gland called pancreas in your body. It is secreted in two different ways. One is called as baseline secretion; in which pancreas secrete 18 to 32 units of insulin throughout the day. This secretion cannot be stopped as it is essential for survival. The other method of insulin secretion depends on food intake. Every time you eat insulin is secreted. It is expected that out of your total insulin requirement, half should come as baseline secretion and half from secretion in response to eating episodes. Whatever you eat, insulin is secreted. It is documented that whether you take less food or more a similar amount of insulin is secreted every time. This we label as individual ‘measure’ of insulin which is person specific. It can be 2 units for one and 12 units for the other. Once insulin is secreted or your measure gets emptied, it takes 55 minutes to refill it. Hence if you eat up to 55 minutes, insulin will be secreted only once. If you continue eating more than 55 minutes, then for every 55 minutes slot you will secrete insulin.
Insulin is a conserving hormone which is responsible for energy storage and processes of synthesis in our body. Every time you eat insulin is secreted. It takes care of the end products of digestion of foods that you consume. Surprisingly, though you eat dozens of food items, the end products are only three: glucose from carbohydrates, amino acids from proteins and fatty acids from fats. On an average we need energy to the tune of 2000 calories per day. 1gm glucose/ 1 gm protein gives 4 calories and 1 gm fatty acids give 9 calories. The cells of the body can use glucose or fatty acids for energy. The trillions of cells in the body except cells from organ like brain are happy burning fatty acids. Brain cells have preference for glucose. Glucose from the blood can not directly enter the cells as there is a lock on each cell, technically called insulin receptor. For glucose to enter the cells, insulin must open the lock of insulin receptors. Then only cells can get glucose. Brain cells are again exception to this as they can directly take glucose from the blood. The first function of insulin is to allow the entry of glucose in cells. Cells then utilize glucose and perform their functions. If there is some more glucose in blood, it is converted to a substance called glycogen in liver and muscles under the influence of insulin. Generally an adult would have 100gm of glycogen reserve in liver. If there is still more glucose in blood, then insulin converts this into fatty acids and stores in body as fats! Insulin converts amino acids into useful proteins and also stores fatty acids as fats in body. Thus it is a conserving hormone responsible for synthesis in the body. Insulin acts a switch to shuffle between use of glucose or fatty acids by the body. If high, body uses glucose and if low, body uses fatty acids as fuel. This is called as day cycle and night cycle in physiology.
Raised level of insulin, technically called as hyperinsulinemia, is responsible for many deleterious effects on our body. There are thousands of research articles published in medical journals that document these effects. These include hypertension, obesity, hyperlipidemia and importantly insulin resistance. Insulin resistance then results into type 2 or maturity onset diabetes mellitus.
When insulin level goes down then first glucose from blood is used by cells for energy. Then glycogen is broken down to get energy. Then your fats are used for energy purpose. One must understand that to use fats for energy one has only one option and that is to reduce insulin level in the body. This can be done not by eating less but by eating less frequently!
Role of insulin in diabetes and obesity
- Insulin Secretion
- Functions Of Insulin
- Effects Of Hyperinsulinemia
- What happens if insulin level goes down?
Insulin is a chemical substance scientifically termed as hormone from a gland called pancreas in your body. It is secreted in two different ways. One is called as baseline secretion; in which pancreas secrete 18 to 32 units of insulin throughout the day. This secretion cannot be stopped as it is essential for survival. The other method of insulin secretion depends on food intake. Every time you eat insulin is secreted. It is expected that out of your total insulin requirement, half should come as baseline secretion and half from secretion in response to eating episodes. Whatever you eat, insulin is secreted. It is documented that whether you take less food or more a similar amount of insulin is secreted every time. This we label as individual ‘measure’ of insulin which is person specific. It can be 2 units for one and 12 units for the other. Once insulin is secreted or your measure gets emptied, it takes 55 minutes to refill it. Hence if you eat up to 55 minutes, insulin will be secreted only once. If you continue eating more than 55 minutes, then for every 55 minutes slot you will secrete insulin.
Insulin is a conserving hormone which is responsible for energy storage and processes of synthesis in our body. Every time you eat insulin is secreted. It takes care of the end products of digestion of foods that you consume. Surprisingly, though you eat dozens of food items, the end products are only three: glucose from carbohydrates, amino acids from proteins and fatty acids from fats. On an average we need energy to the tune of 2000 calories per day. 1gm glucose/ 1 gm protein gives 4 calories and 1 gm fatty acids give 9 calories. The cells of the body can use glucose or fatty acids for energy. The trillions of cells in the body except cells from organ like brain are happy burning fatty acids. Brain cells have preference for glucose. Glucose from the blood can not directly enter the cells as there is a lock on each cell, technically called insulin receptor. For glucose to enter the cells, insulin must open the lock of insulin receptors. Then only cells can get glucose. Brain cells are again exception to this as they can directly take glucose from the blood. The first function of insulin is to allow the entry of glucose in cells. Cells then utilize glucose and perform their functions. If there is some more glucose in blood, it is converted to a substance called glycogen in liver and muscles under the influence of insulin. Generally an adult would have 100gm of glycogen reserve in liver. If there is still more glucose in blood, then insulin converts this into fatty acids and stores in body as fats! Insulin converts amino acids into useful proteins and also stores fatty acids as fats in body. Thus it is a conserving hormone responsible for synthesis in the body. Insulin acts a switch to shuffle between use of glucose or fatty acids by the body. If high, body uses glucose and if low, body uses fatty acids as fuel. This is called as day cycle and night cycle in physiology.
Raised level of insulin, technically called as hyperinsulinemia, is responsible for many deleterious effects on our body. There are thousands of research articles published in medical journals that document these effects. These include hypertension, obesity, hyperlipidemia and importantly insulin resistance. Insulin resistance then results into type 2 or maturity onset diabetes mellitus.
When insulin level goes down then first glucose from blood is used by cells for energy. Then glycogen is broken down to get energy. Then your fats are used for energy purpose. One must understand that to use fats for energy one has only one option and that is to reduce insulin level in the body. This can be done not by eating less but by eating less frequently!
Why Diet Plans Fail?
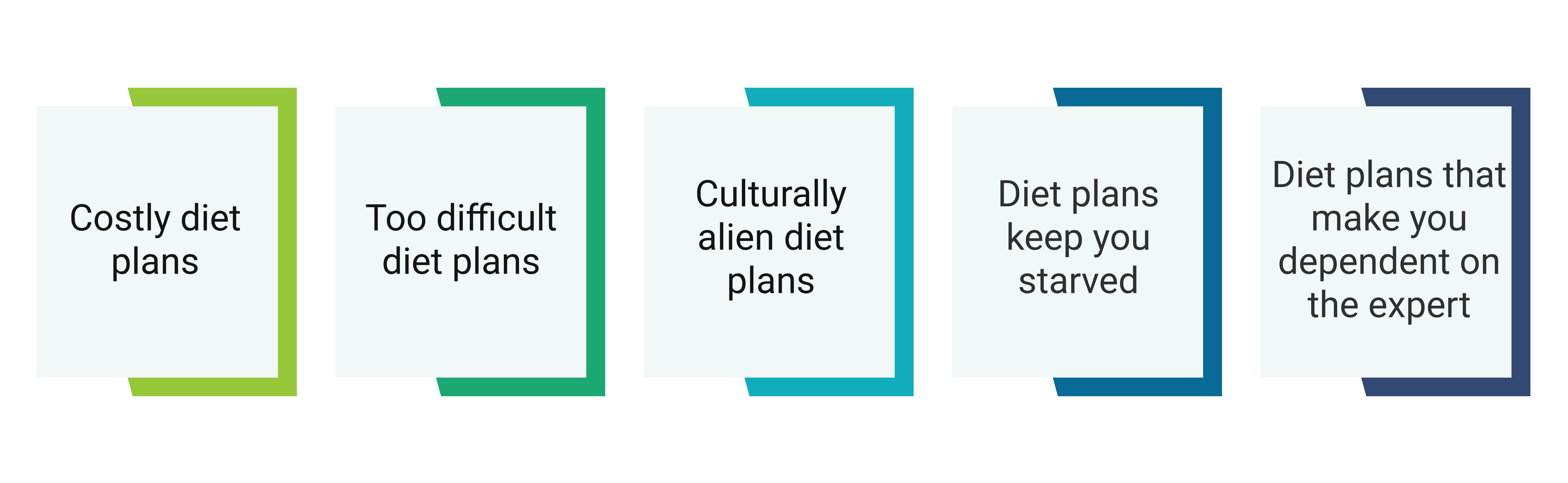

And most importantly, you are exploited by weight loss industry because of your mentality that ‘someone else will/can reduce your weight’!
Importance of getting HbA1C and fasting insulin tests done
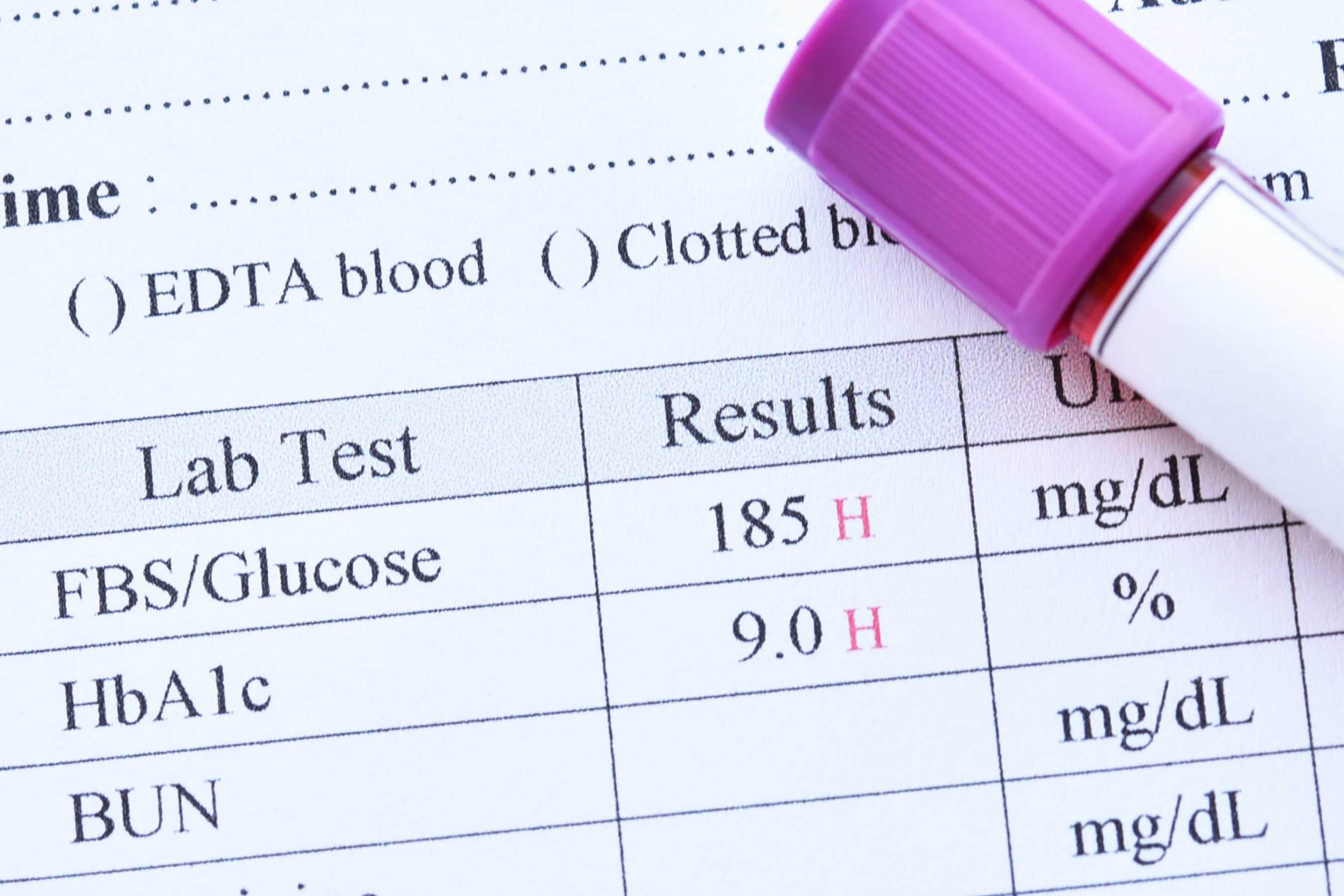
HbA1C gives us the average blood sugar of last three months. Compared to fasting and post meal blood sugars, it is a more robust indicator of blood glucose levels. As most doctors suspect diabetes on the basis of blood sugars, around 30% cases of prediabetes are missed! Hence HbA1C is recommended in this lifestyle modification. When you are in fasting state, your insulin should be near zero. It should be at least below ten. In some countries a value above ten is considered as prediabetes. Make sure that your laboratory technician has understood the difference between fasting blood sugar and fasting insulin. It is likely that he may provide you results of fasting blood sugar rather than fasting insulin!
How to interpret the test results?
- HbA1C up to 5.6 is regarded as normal.
- From 5.7 to 6.4 it is labelled as prediabetes and after 6.5 it is called as diabetes.
- Fasting insulin in healthy nondiabetic person should be near zero or at least below ten.
- More than ten is labelled as prediabetes in this campaign.

HbA1C up to 5.6 is regarded as normal. From 5.7 to 6.4 it is labelled as prediabetes and after 6.5 it is called as diabetes. Fasting insulin in healthy nondiabetic person should be near zero or at least below ten. More than ten is labelled as prediabetes in this campaign.
Simple Method to Lose Weight and Prevent Diabetes
It is clear that if you wish to lose weight and your protruding tummy, then the only way available is to reduce frequency of insulin secretion. Generally we feel really hungry only twice in the day. So the simple method to lose weight and prevent diabetes includes following suggestions:
- Non Diabetic:
- Identify two times when you are really hungry. If you can’t identify then adopt 9am, 6pm or 1pm, 9pm timings for taking meals. In a week with trial and error you will settle down on your real times.
- As far as possible keep the meal times fixed
- Do not eat anything in between two meals
- Finish your meal in maximum time of 55 minutes
- Reduce sweets from your meals
- Increase proteins in your diet
- Pre-Diabetic and Diabetic
- Identify two times when you are really hungry. If you can’t identify then adopt 9am, 6pm or 1pm, 9pm timings for taking meals. In a week with trial and error you will settle down on your real times.
- As far as possible keep the meal times fixed
- Do not eat anything in between two meals
- Finish your meal in maximum time of 55 minutes
- No Sugar or Fruits for first 3 months of diet plan
- Increase proteins in your diet
- Non Diabetic
- Water
- Thin home-made buttermilk (make 200 ml buttermilk from 10 to 15 ml of curd)
- Tea with 25% milk and 75% water, black tea or green tea (all without sugar or sugar substitutes)
- Tender coconut water (Don’t eat pulp. Eat it in your meal time!)
- Maximum one tomato in a day.
- Pre-Diabetic and Diabetic
- Water
- Thin home-made buttermilk (make 200 ml buttermilk from 10 to 15 ml of curd)
- black tea or green tea (all without sugar or sugar substitutes)
Recommended exercise

The recommended exercise in this lifestyle modification is to walk 4.5 Km in 45 minutes at a stretch for at least 5 days a week. Cycling and swimming for 45 minutes at a stretch are the other options. Other exercises like Yogasanna and weight training are other options.
